Resay Technologies Delivery Tracker
Internal Mail & Parcel Tracking Software Once loaded on to a stand alone PC or hand held terminal, this software offers users the ability to track and trace all incoming and out-going mail and packages, making it the ideal solution for multi-department offices, large sites and NHS organisations.
Read moreResay Technologies Bartender
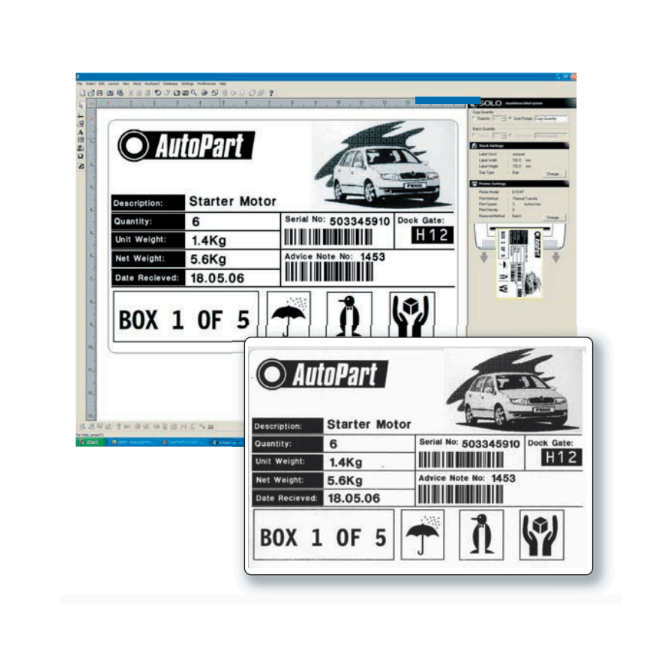
Label Printing Software for Barcode Printers BarTender barcode software is the world's leading design and print software for labels, barcodes, cards and RFID tags. Running stand-alone or integrated with just about any other program
Read moreResay Technologies Food Software
Resay is an automated hand held system that enables you to quickly and accurately monitor and record all aspects of your food handling operations. Resay has been around for over 20 years and is extremely flexible. Resay is designed to be used by any food business including manufacturers, distributors, retailers, hotels, restaurants, pubs, fast food outlets, schools and many others.
Read moreResay Technologies Stock Master for Sage
Designed to address the most common data collection requirements including:
- Goods In
- Stock Taking
- Mobile Point of Sale
- Sage Invoicing
- Order Picking & Packing
Resay Technologies Mobile Worker
Offering you the ability to import any CSV or Excel file onto your your Windows based batch or WiFi terminals, Mobile Worker software will recreate an exact replica of the CSV or Excel file on screen - allowing you to populate the file with the exact information you need in the correct file location.
Read moreResay Technologies RT Direct Label Software
Labelling with the direct advantage
Read moreResay Technologies RT Retail Software
Retail & Convenience Store EPOS Software
Read moreResay Technologies TimeView
Time and Attendance Solution
Read moreResay Technologies CTI Comet USB
Caller ID The CTI Comet USB is a Caller ID unit with USB connectivity Ideally suited for Epos terminals, fast food outlets, taxi companies and Doctors or Dental surgiers
Read more”Software” refers to a set of instructions or programs that enable a computer or other digital device to perform specific tasks or functions. It encompasses a wide range of applications, systems, utilities, and programs that contribute to the functionality of computers and electronic devices. Here are some key categories and types of software:
- Operating Systems (OS):
- Examples: Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, iOS.
- Function: Manages hardware resources, provides user interfaces, and supports the execution of other software.
- System Software:
- Examples: Device drivers, utilities, firmware.
- Function: Supports the operation of computer hardware and provides essential services for computer programs.
- Application Software:
- Examples: Word processors, web browsers, graphic design software, games.
- Function: Enables users to perform specific tasks or create content. Applications are designed for various purposes, such as productivity, entertainment, or communication.
- Programming Softwares:
- Examples: Integrated Development Environments (IDEs), compilers, debuggers.
- Function: Tools used by programmers to write, test, and debug software code.
- Utilities:
- Examples: Antivirus software, disk cleaners, backup tools.
- Function: Provides additional functionalities to enhance system performance, security, and maintenance.
- Middleware:
- Examples: Database management systems, web servers.
- Function: Connects software components or applications, allowing them to communicate and share data.
- Device Drivers:
- Examples: Printer drivers, graphics drivers.
- Function: Enables communication between the operating system and hardware devices, ensuring proper functionality.
- Firmware:
- Examples: BIOS/UEFI firmware, device firmware.
- Function: Embedded softwares that provides low-level control for specific hardware components.
- Business Softwares:
- Examples: Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), Customer Relationship Management (CRM), accounting software.
- Function: Supports business processes and operations, facilitating organization-wide tasks.
- Productivity Softwares:
- Examples: Microsoft Office (Word, Excel, PowerPoint), Google Workspace.
- Function: Aids users in creating, editing, and managing documents, spreadsheets, presentations, and other content.
- Security Softwares:
- Examples: Antivirus, anti-malware, firewalls.
- Function: Protects computers and networks from malicious software and unauthorized access.
- Educational Softwares:
- Examples: Learning management systems, educational games.
- Function: Facilitates learning and educational activities through interactive content and tools.
- Graphics and Multimedia Softwares:
- Examples: Adobe Photoshop, VLC Media Player.
- Function: Enables the creation, editing, and playback of visual and multimedia content.
- Communication Softwares:
- Examples: Email clients, instant messaging apps.
- Function: Facilitates communication and collaboration between users through digital platforms.
- Entertainment Softwares:
- Examples: Video games, streaming services.
- Function: Provides entertainment through interactive games, movies, music, and other digital content.
Softwares is a fundamental component of modern computing, enabling users to perform a wide range of tasks and functions. It can be categorized based on its purpose, functionality, and target audience, and it continues to evolve with advancements in technology.