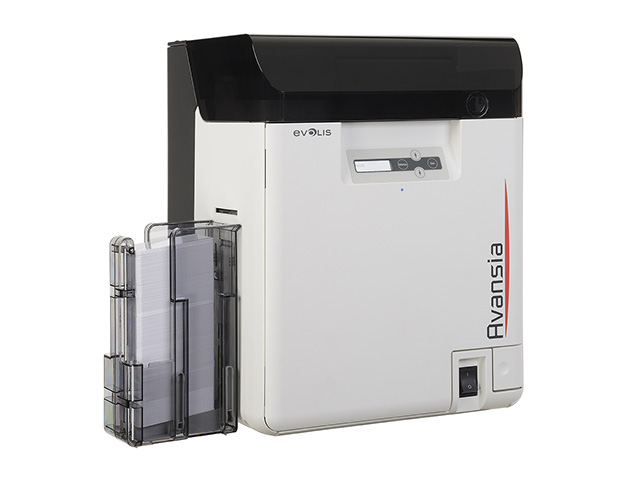
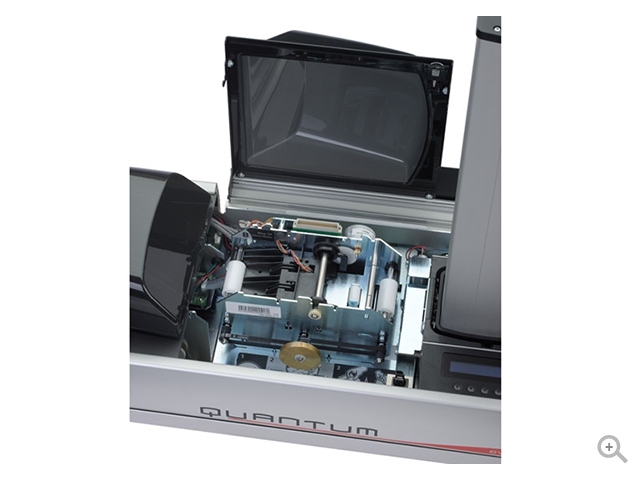
Card printers, also known as ID card printers or badge printers, are specialized devices designed for printing identification cards, access cards, membership cards, and various types of plastic cards. These printers are widely used in industries such as corporate security, education, healthcare, and government for producing personalized and secure identification cards. Here are key aspects associated with card printers:
- Card Printing Technologies:
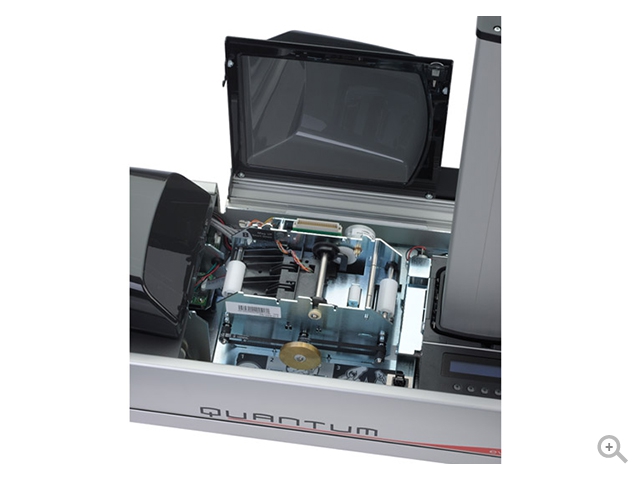
- Direct-to-Card (DTC) Printing: This common technology involves transferring ink directly onto the surface of the card using a thermal print head. DTC printers are suitable for standard ID cards.
- Retransfer Printing: This technology involves printing the image on a clear film, which is then fused onto the card surface using heat and pressure. Retransfer printing is known for producing high-quality and durable prints.
- Single-Sided vs. Dual-Sided Printing:
- Card printers can be configured for single-sided or dual-sided printing. Dual-sided printers are capable of printing on both sides of the card, allowing for additional information or security features.
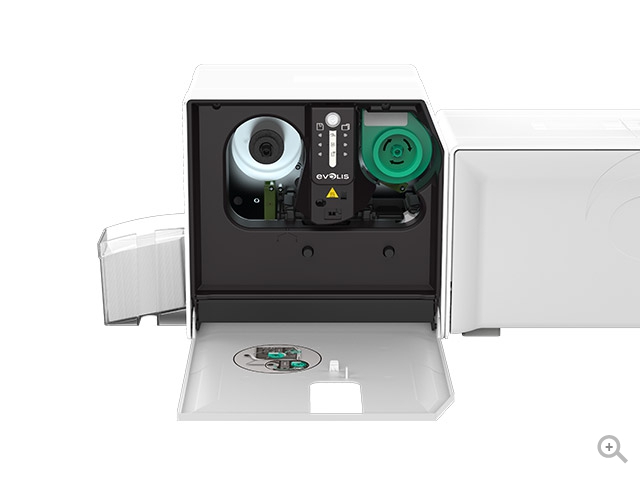
- Card Encoding:
- Some card printers offer encoding capabilities, allowing for the integration of magnetic stripes, smart chips, or radio-frequency identification (RFID) technology into the cards for access control or other applications.
- Card Material Compatibility:
- Card printers are designed to work with different card materials, including PVC, polyester, and composite materials. The compatibility with various card materials ensures flexibility in card design and durability.
- Print Resolution:
- Print resolution is measured in dots per inch (dpi) and determines the level of detail in the printed image. Higher dpi values result in sharper and more detailed card prints.
- Color Printing:
- Card printers can produce cards in full color, allowing for the incorporation of logos, images, and other design elements. High-quality color printing is essential for creating visually appealing and professional-looking ID cards.
- Card Security Features:
- Many card printers offer security features such as holographic overlays, UV printing, and watermarking to enhance the security and authenticity of the printed cards.
- Card Design Software:
- Card printers often come with or support card design software that allows users to create and customize card layouts. These software tools enable the inclusion of text, images, and variable data on the cards.
- Connectivity:
- Card printers typically connect to computers and networks via USB, Ethernet, or wireless interfaces. This connectivity facilitates seamless integration into existing systems for card issuance.
- Batch Printing:
- Batch printing capabilities allow card printers to efficiently produce a large number of cards in a single printing session. This is particularly useful for organizations that need to issue cards in bulk.
- Card Lamination:
- Some card printers come with lamination modules that apply a protective layer to the printed cards, enhancing durability and resistance to wear and tear.
- User-Friendly Interface:
- Card printers often feature user-friendly interfaces for easy operation. This includes LCD screens, touch panels, and intuitive software interfaces for managing card printing settings.
- Environmental Considerations:
- Energy-efficient and eco-friendly features, such as sleep modes and reduced power consumption, are increasingly important considerations for card printers.